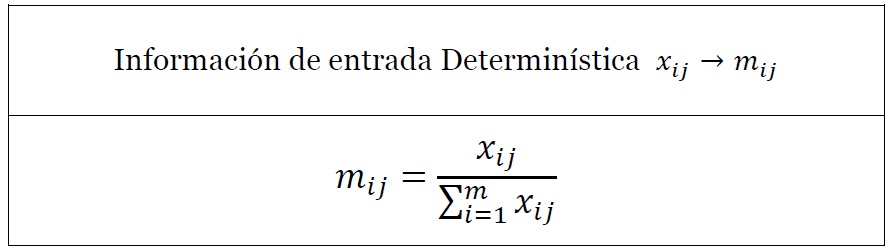
Cuando nos enfrentamos a problemas de causalidad complejos y difíciles de articular o comprender, un enfoque habitual para su estudio es la aplicación de un modelo. El modelo DEMATEL (Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory) fue creado en el Instituto Battelle de Ginebra en 1971.
Cuando nos enfrentamos a problemas de causalidad complejos y difíciles de articular o comprender, un enfoque habitual para su estudio es la aplicación de un modelo. El modelo DEMATEL (Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory) fue creado en el Instituto Battelle de Ginebra en 1971.
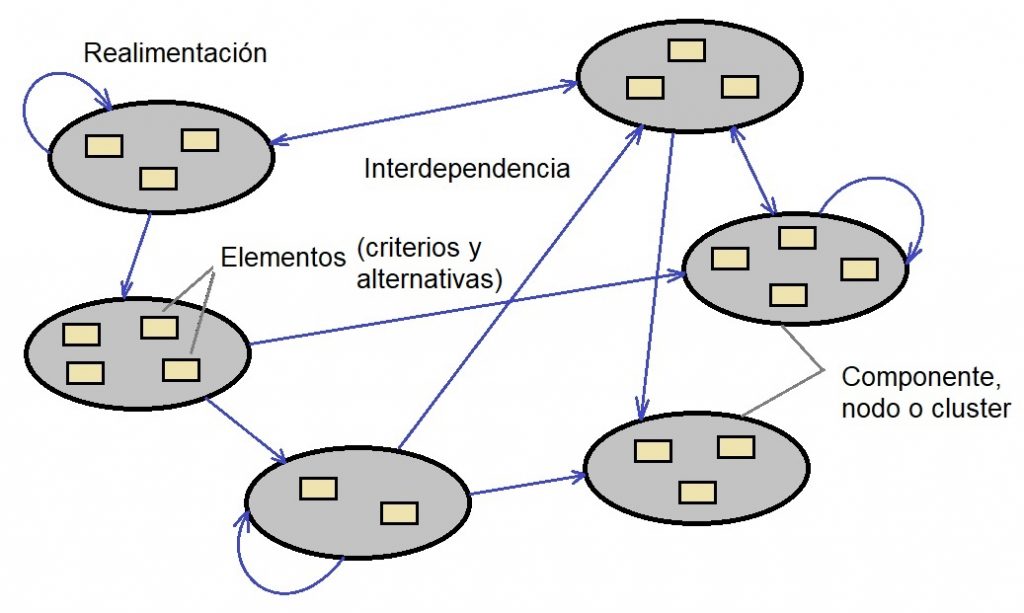
Se trata de un modelo especialmente útil para analizar las relaciones de causa y efecto entre los componentes de un sistema. Esta propuesta permite confirmar la interdependencia entre factores y ayudar a elaborar un mapa que refleje las relaciones relativas entre ellos, y puede utilizarse para investigar y resolver problemas complicados y entrelazados. Este método no solo convierte las relaciones de interdependencia en un grupo de causa y efecto mediante matrices, sino que también encuentra los factores críticos de un sistema de estructura compleja con la ayuda de un diagrama de relaciones de impacto.
DEMATEL, al igual que ANP (Analytic Network Process), se basa en las percepciones de los individuos (una persona o un grupo de personas). En todos los casos encontrados en la literatura, DEMATEL y ANP se utilizan para crear una supermatriz ponderada, que se potencia hasta el límite para obtener las prioridades de los factores/alternativas de decisión relevantes. Lo interesante es que DEMATEL presenta grandes ventajas al usarlo con ANP, pues identifica realimentaciones e interdependencias en la red y simplifica en gran manera el cálculo en red al sustituir las matrices de comparación pareada por una escala de cero a tres que permite plantear de inicio una matriz de relación directa. Ninguna influencia se puntúa como 0, 1 es la valoración para una influencia leve, 2 para una influencia fuerte y 3 para una influencia muy fuerte. No obstante, hay autores que proponen una escala de 0 a 4.
Los pasos necesarios para aplicar DEMATEL son los siguientes:
- Construcción de la matriz de influencia directa
- Normalización de la matriz de influencia directa
- Encontrar la matriz de relación total
- Producción de un diagrama causal
- Obtención de la matriz de dependencia interna y el mapa de relación de impacto
En los siguientes vídeos del profesor Aznar se explican en detalle la mecánica de cálculo. Espero que os sean de interés. Para aquellos interesados, los vídeos forman parte de un pequeño curso gratuito MOOC al que podéis acceder en este enlace:
https://www.edx.org/es/course/valoracion-de-activos-por-metodos-multicriterio
Referencias:
AZNAR, J. (2020). Curso de valoración de activos por métodos multicriterio AHP, ANP y CRITIC. Editorial Universitat Politècnica de València. Ref. 264.
BERNAL, S.; NIÑO, D.A. (2018). Modelo multicriterio aplicado a la toma de decisiones representables en diagramas de Ishikawa. Universidad Distrital Francisco José de Caldas, Bogotá D.C., 137 pp.
SAATY, T.L. (1980). The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation, McGraw-Hill.
SAATY, T.L., VARGAS, L. G. (2013). Decision making with the analytic network process: economic, political, social and technological applications with benefits, opportunities, costs and risks (Vol. 195). Springer Science & Business Media

Esta obra está bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.;